The big questions for China macro policy this year
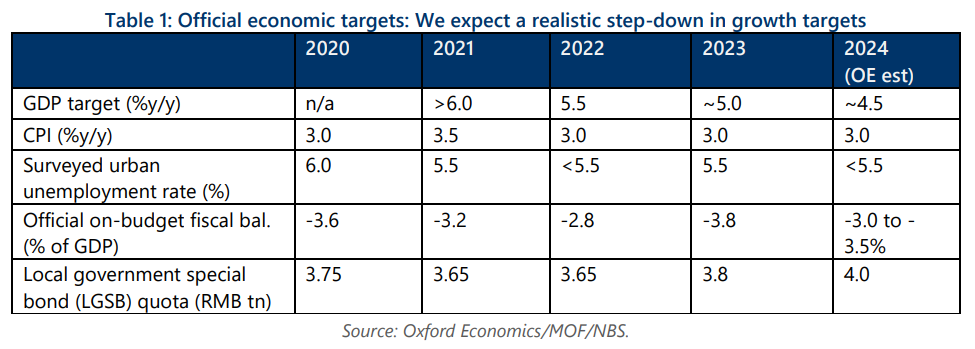
Ahead of this spring’s Two Sessions, we expect officials to realistically stake their growth target at around 4.5% in 2024 – a more sustainable, though likely still above-potential, pace than in 2023. Risks to our baseline forecast are titled to the upside, as fiscal easing could prove more forthcoming, and the poor performance of exports could improve. This report analyses some of the key questions regarding China macro policies in 2024.
What you will learn:
- Fiscal stimulus in 2024 will include greater support for policy banks, tax waivers, and other cost-offsets for businesses, plus spending on both old and new infrastructure. Quasi-fiscal tools, such as the pledged supplementary lending (PSL) facility, will also play a bigger role.
- Broad-based, direct support for household consumption still seems unlikely, even as China grapples with a confidence crisis. We expect private consumption to slow to a respectable 5.2% in 2024, from an estimated 8.7% in 2023.
- Property easing will likely continue in the form of further liquidity injections into policy banks for housing projects, more direct subsidies to improve housing affordability and induce consumers to purchase homes, and a restructuring of property developer balance sheets to liquidate high inventory and bad loans with the assistance of state banks.
- Although accommodative monetary policies are necessary, the room for a further meaningful decline in rates is limited.
- We expect a mild appreciation of the renminbi deeper into H2, ending 2024 at 7.0 to the dollar on narrowing US-China rate differentials, stabilizing domestic fundamentals, a smaller current account surplus, and continued spot intervention from the PBOC to stem depreciation pressures.
Tags:
Related Posts

Post
Tariffs 101: What are they and how do they work?
Tariffs are taxes imposed by a government on goods and services imported from other countries. Think of tariff like an extra cost added to foreign products when they enter the country. They’re usually a percentage of the price of the goods, making imported items more expensive compared to domestically produced good
Find Out More
Post
Global Scenarios Service – Heightened Tensions
This quarter’s scenarios quantify key risks to the global economy. These relate primarily to trade protectionism and other geopolitical tensions, structural weakness in the Chinese economy, the stance of monetary and fiscal policy, and financial market conditions.
Find Out More
Post
U.S. dollar strength to remain; Fed to hold interest rates until December
Innes McFee, Managing Director of Macroeconomic and Investor Services at Oxford Economics, discusses the outlook for the U.S. dollar and adds that tariffs will be a “negative” for the U.S. economy.
Find Out More