Japan’s BoJ postponed a rate hike to analyse more data
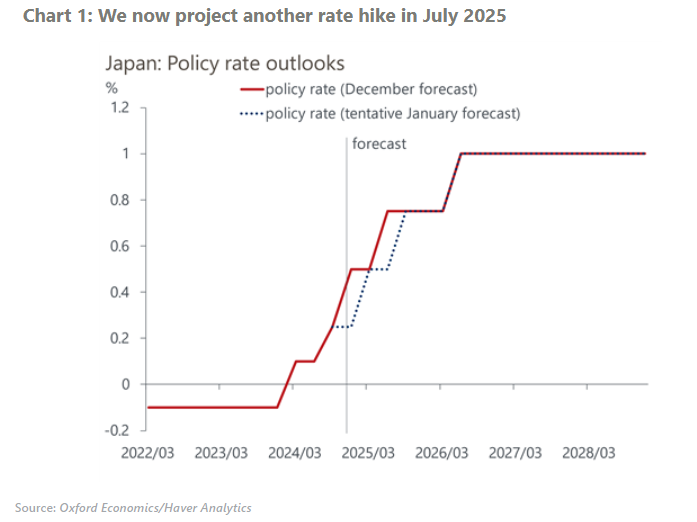
The Bank of Japan kept its policy rate at 0.25% at Thursday’s meeting, as we expected. We believe that the central bank will raise the policy rate to 0.5% in January 2025 and to 0.75% after confirming the strong outcome of the Spring Wage Negotiation next year, most likely in July.
What you will learn:
- The BoJ is waiting for more data to confirm the momentum of the wage-driven inflation dynamics. Although scheduled earnings have increased at a rate roughly consistent with 2% inflation, data on consumption has been mixed amid lacklustre real income growth.
- We project another strong wage increase of around 4.5% in 2025, slightly less than 5.1% this year. Risks are tilted to upside. SMEs will generally manage to follow the wage increases by leading large firms, but more unprofitable firms will start to fall behind the overall wage growth trend.
- We project that rising wages will gradually raise CPI inflation after it slows to around 1.5% by mid-2025 due to the base effect of past inflation. We are more cautious than the BoJ on how much firms, especially SMEs, will manage to pass on rising wage costs to final prices.
Tags:
Related Posts

Post
Japan’s on course for July rate hike, but risk of June increases
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) kept its policy rate at 0.50% at Wednesday's meeting, as expected. Despite a marginally higher increase in pay than last year at the first round of the spring wage negotiations, our baseline view is for the BoJ to hike its policy rate only gradually due to concerns about the capacity of small firms to raise wages and the lacklustre rate of consumption.
Find Out More
Post
Japan’s supply-driven food inflation to persist longer than expected
We have revised our CPI forecast upwards for this year and next, due to more persistent supply side-driven food inflation, led by soaring prices of rice. Despite the significant revision to the short-term inflation path, we don't expect the Bank of Japan (BoJ) to react with a rate hike.
Find Out More
Post
Japan’s older households to support spending under higher rates
The resilience of consumption is essential to support sustained wage-driven inflation and the Bank of Japan's rate hikes. We see little risk of spending faltering due to the projected gradual rate hikes to 1% because the ageing of society has made households' balance sheets less vulnerable to rate increases.
Find Out More