Japan’s supply-driven food inflation to persist longer than expected
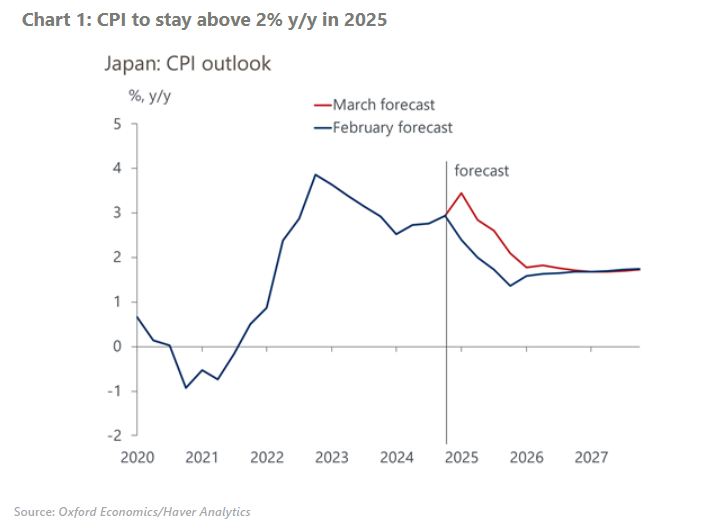
We have revised our CPI forecast upwards for this year and next, due to more persistent supply side-driven food inflation, led by soaring prices of rice. Despite the significant revision to the short-term inflation path, we don’t expect the Bank of Japan (BoJ) to react with a rate hike.
What you will learn:
- A combination of record summer heat in 2023, panic buying, and speculative trading has driven rice prices upwards. Despite a good harvest in 2024 and the government’s decision to sell its rice stockpiles, prices are still rising and we now expect them to decline more slowly than we previously anticipated.
- The prices of non-fresh foods other than rice have also registered modest but persistent inflation, of 3%-4%, reflecting the pass-through of rising input costs, including the lagged impact of yen weakening and a sharp rise in logistics costs.
- We have not changed our monetary policy forecast since the supply-driven food inflation, especially rising rice prices, will likely stabilise. That said, we will closely monitor how higher food inflation affects inflation expectations. We have nudged up our 10-year Japanese government bond (JGB) forecast to reflect a higher inflation risk premium.
Tags:
Related Posts

Japan’s older households to support spending under higher rates
The resilience of consumption is essential to support sustained wage-driven inflation and the Bank of Japan's rate hikes. We see little risk of spending faltering due to the projected gradual rate hikes to 1% because the ageing of society has made households' balance sheets less vulnerable to rate increases.
Find Out More
Japan’s small firms’ profitability will help determine further rate hikes
Rising wage costs have been increasingly squeezing the already low profitability of small firms in Japan, thereby raising concerns about the sustainability of the wage-driven inflation dynamics. The evolution of these dynamics will be key in determining how far the Bank of Japan can raise its policy rate in the coming years
Find Out More
Autos and machineries in Japan are most vulnerable to US tariffs
Our analysis of industry and trade structure between the US and Japan reveals the auto and non-electrical machinery sectors are most vulnerable to tariffs by the US. For both sectors, the US accounts for a sizeable share of total exports as well as gross output, and particularly so for auto.
Find Out More