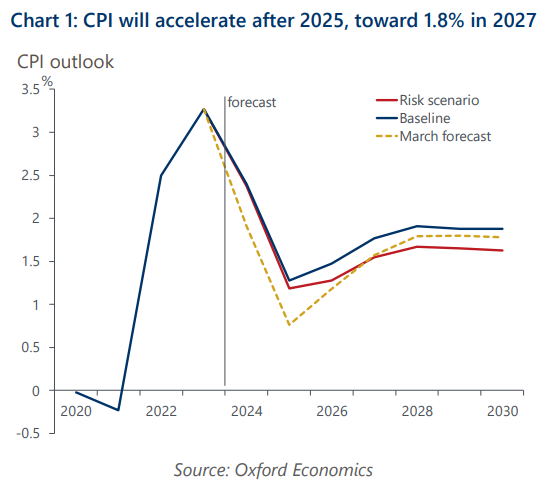
Japan inflation to rise to 1.8%, but downside risks are high
Reflecting a surprisingly strong Spring Negotiation result and weaker yen assumption, we have upgraded our baseline wage and inflation forecasts. We now project higher wage settlements will push inflation towards 1.8% by 2027. Uncertainty is high, however.
What you will learn:
- We anticipate the final outcome of the Spring Negotiation this year will likely be a wage rise of around 4.5% or more – much higher than last year’s 3.6%. We upgraded our wage projections for the next few years to reflect more aggressive wage-setting behaviour by top-tier firms.
- The main downside risk to our outlook is the sustainability of wage increases by SMEs. Another downside risk is disappointing demand growth, which will constrain pricing power.
- In our downside scenario, which assumes that these inter-related downside risks materialise, we project the CPI inflation rate would stabilise at 1.6% in 2027.
Tags:
Related Posts

Post
Japan’s politics add uncertainty to BoJ policy outlook
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) kept its policy rate at 0.5% at its October meeting, after a 7-2 majority vote. Two board members again voted for a rate increase. We believe the BoJ will hike in December to 0.75% as incoming data confirm that the economy is performing in line with the bank's forecasts in its quarterly outlook. However, there's a material chance of a delay.
Find Out More
Post
Japan’s December rate hike appears likely, though there is a risk of delay
We've brought forward the timing of the next Bank of Japan (BoJ) 25bps rate hike to December from next year and have added another 25bps hike in mid-2026. This reflects the surprisingly hawkish shift in the BoJ's view since its September policy meeting and upward revisions to our growth and inflation projections, driven by the US economy's resilience.
Find Out More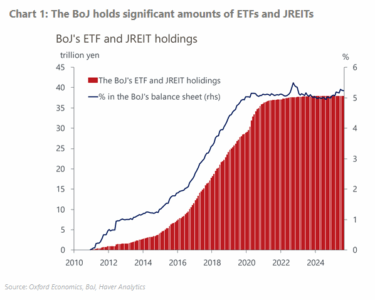
Post
BoJ announces cautious plan to sell ETF and J-REIT holdings
At its monetary policy meeting on Friday, the Bank of Japan (BoJ) unexpectedly announced it would start to sell its ETF and Japanese real estate investment trust (J-REIT) holdings. We think the impact of this plan on financial markets will likely be limited because the BoJ is opting to play it safe in terms of the process and the scale.
Find Out More