Major China cities face prospect of growth downshift
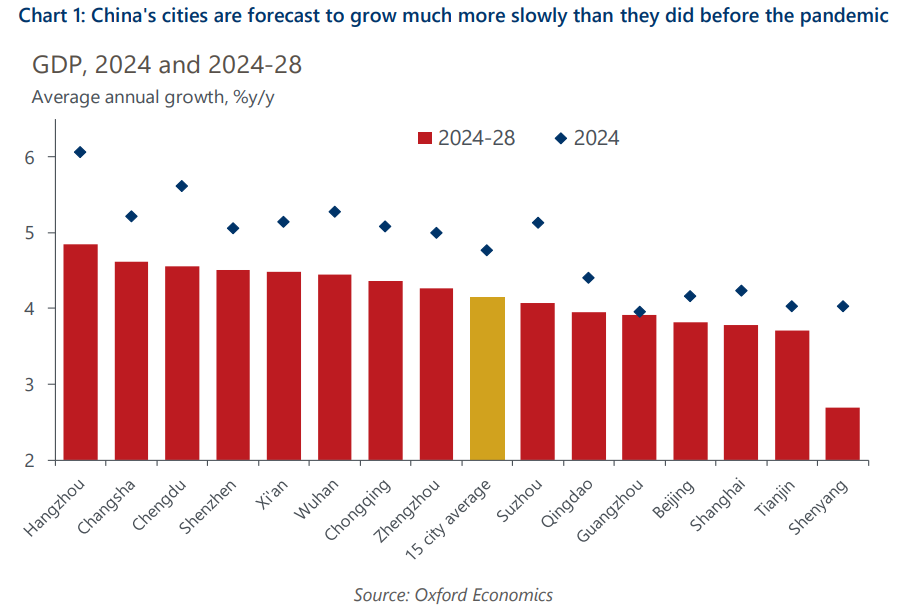
Over the next five years China and its major cities face the prospect of a significant downshift in economic growth. We forecast GDP to grow on average by 4.1% per year across 15 major cities in the years to 2028, down from 7.3% between 2015-2019.
What you will learn:
- A key challenge facing China and its cities in the medium term is finding an engine for growth at a time when the country’s property sector is at a low ebb. Although real estate activity is typically a small sector for each city, it has linkages to other sectors, such a construction. These sectors will likely underperform in most cities in the next five years.
- China’s government instead places the emphasis of invigorating the country’s economic growth on its “new productive forces” of advanced IT services, and high-tech manufacturing. Cities with strength in these sectors, particularly the coastal tech cities of Shenzhen and Hangzhou, appear towards the top of our major city GDP growth rankings over the next five years.
- However, the significant regional imbalance in the concentration of these industries means some cities are at risk of being left behind. Qingdao, Shenyang, and others with economies that are largely entrenched in China’s traditional industrial base are forecast to feature further down the growth rankings.
Tags:
Related Posts

Post
Which regions are most exposed to the 25% automotive tariffs?
While the automotive tariffs will likely lead to some production being reshored to US plants, they will also raise costs for US manufacturers and households.
Find Out More
Post
Parsing US federal job cuts by metro
Cuts to the Federal government workforce, which we estimate to be 200,000 in 2025, will have a modest impact nationally, but more significant implications for the Washington, DC metropolitan economy as it accounts for 17% of all non-military federal jobs in the US.
Find Out More
Post
The European housing market has turned a corner, but challenges remain
The housing market across most of Europe has now improved, but has it reached the tipping point?
Find Out More