Surprisingly strong wage data ends NIRP and YCC in Japan
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) decided to end its negative interest rates policy and set the target band for the overnight market rate at 0%-0.1% at Tuesday’s meeting, earlier than our call for April. The first tally of the Spring Wage Negotiation, mainly for leading firms, was surprisingly strong, making the Bank confident about the wage-driven path to its 2% inflation target in coming years.
What you will learn:
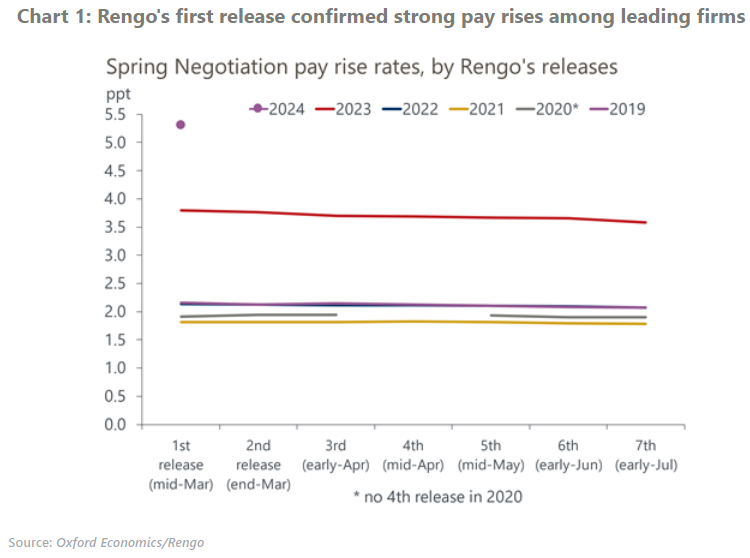
- In the first tally, the headline pay rise rate was 5.3%, much higher than the 3.8% in 2023 and market expectations. As the wage settlement for smaller firms become available, the pay rise rate will likely decline, converging to 4.5% which is the pay rise rate for small firms in the first tally.
- In order to guide market expectation for next policy moves, the policy statement said that “given the current outlook for economic activities and prices, the Bank anticipates accommodative financial condition will be maintained for the time being.” We anticipate the BoJ will maintain an effective zero-interest rate policy at least for another year.
- The BoJ also dismantled the yield curve control framework, which had increasingly become a formality after a decision in October 2023 to make it more flexible. In order to avoid disruptions in long-term yields, the bank commits to keep purchasing Japanese government bonds (JGB) close to its current pace for now, and promises to intensely increase them upon sharp yield rises.
- While committing to continue a quantitative easing (QE) policy through JGB purchases, the BoJ decided to formally end the purchase of risky assets such as ETFs and REITs which have not taken place for several months. We believe that the BoJ will come up with a comprehensive exit strategy from QE policy later this year after its ongoing policy review.
Tags:
Related Posts

Post
25% auto tariffs especially painful in Japan and South Korea
US tariffs of 25% on all automobile and auto parts will weigh heavily on the Japanese and South Korean automotive sectors. A GTAP analysis suggests Japanese and South Korean automotive production will each shrink by approximately 7%. The impact is larger than suggested by bilateral trade data, because vehicles assembled in other countries before being shipped to the US will also be affected, dampening domestic auto parts production.
Find Out More
Post
‘Liberation Day’ 24% tariff will limit Japan’s growth
The 'Liberation Day' tariffs, together with separately announced higher tariffs on auto imports to the US, will lead us to cut our growth forecast for Japan. The direct impact of the tariffs will end the modest growth we projected in March, and we now think the economy will barely grow in 2025-2026. This initial estimate does not consider the indirect impact from high trade policy uncertainty and retaliation from other economies.
Find Out More
Post
Japan’s on course for July rate hike, but risk of June increases
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) kept its policy rate at 0.50% at Wednesday's meeting, as expected. Despite a marginally higher increase in pay than last year at the first round of the spring wage negotiations, our baseline view is for the BoJ to hike its policy rate only gradually due to concerns about the capacity of small firms to raise wages and the lacklustre rate of consumption.
Find Out More