Why we forecast Japan’s resilient growth in 2023
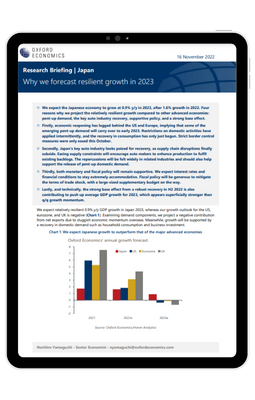
We expect the Japanese economy to grow at 0.9% y/y in 2023, after 1.6% growth in 2022. Four reasons why we project the relatively resilient growth compared to other advanced economies: pent-up demand, the key auto industry recovery, supportive policy, and a strong base effect.
What you will learn:
- Firstly, economic reopening has lagged behind the US and Europe, implying that some of the emerging pent-up demand will carry over to early 2023.
- Secondly, Japan’s key auto industry looks poised for recovery, as supply chain disruptions finally subside. Easing supply constraints will encourage auto makers to enhance production to fulfil existing backlogs.
- Thirdly, both monetary and fiscal policy will remain supportive. We expect interest rates and financial conditions to stay extremely accommodative.
- Lastly, and technically, the strong base effect from a robust recovery in H2 2022 is also contributing to push up average GDP growth for 2023, which appears superficially stronger than q/q growth momentum.
Tags:
Related Resouces

Post
25% auto tariffs especially painful in Japan and South Korea
US tariffs of 25% on all automobile and auto parts will weigh heavily on the Japanese and South Korean automotive sectors. A GTAP analysis suggests Japanese and South Korean automotive production will each shrink by approximately 7%. The impact is larger than suggested by bilateral trade data, because vehicles assembled in other countries before being shipped to the US will also be affected, dampening domestic auto parts production.
Find Out More
Post
‘Liberation Day’ 24% tariff will limit Japan’s growth
The 'Liberation Day' tariffs, together with separately announced higher tariffs on auto imports to the US, will lead us to cut our growth forecast for Japan. The direct impact of the tariffs will end the modest growth we projected in March, and we now think the economy will barely grow in 2025-2026. This initial estimate does not consider the indirect impact from high trade policy uncertainty and retaliation from other economies.
Find Out More
Post
Japan’s on course for July rate hike, but risk of June increases
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) kept its policy rate at 0.50% at Wednesday's meeting, as expected. Despite a marginally higher increase in pay than last year at the first round of the spring wage negotiations, our baseline view is for the BoJ to hike its policy rate only gradually due to concerns about the capacity of small firms to raise wages and the lacklustre rate of consumption.
Find Out More